Py5Vector.lerp()#
Calculates a vector between two vectors at a specific increment.
Examples#
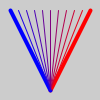
def setup():
v1 = py5.Py5Vector(40, -80)
c1 = py5.color(255, 0, 0)
v2 = py5.Py5Vector(-40, -80)
c2 = py5.color(0, 0, 255)
py5.translate(50, 90)
py5.stroke_weight(4)
py5.stroke(c1)
py5.line(0, 0, v1.x, v1.y)
py5.stroke(c2)
py5.line(0, 0, v2.x, v2.y)
py5.stroke_weight(1)
for i in range(1, 10):
v = v1.lerp(v2, i / 10)
c = py5.lerp_color(c1, c2, i / 10)
py5.stroke(c)
py5.line(0, 0, v.x, v.y)
Description#
Calculates a vector between two vectors at a specific increment. The two vectors must have the same dimension. The amt parameter is the amount to interpolate between the two values where 0.0 equal to the first point, 0.1 is very near the first point, 0.5 is half-way in between, etc. If the amt parameter is greater than 1.0 or less than 0.0, the interpolated vector will be outside of the range specified by the two vectors.
This method is similar to lerp() and lerp_color(), but for vectors instead of numbers or colors.
Signatures#
lerp(
other: Union[Py5Vector, np.ndarray], # other vector to interpolate between
amt: Union[float, np.ndarray], # float between 0.0 and 1.0
) -> Union[Py5Vector, np.ndarray[np.floating]]
Updated on March 06, 2023 02:49:26am UTC
