bezier_tangent()#
Calculates the tangent of a point on a Bezier curve.
Examples#
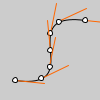
def setup():
py5.no_fill()
py5.bezier(85, 20, 10, 10, 90, 90, 15, 80)
steps = 6
py5.fill(255)
for i in range(0, steps+1):
t = i / steps
# get the location of the point
x = py5.bezier_point(85, 10, 90, 15, t)
y = py5.bezier_point(20, 10, 90, 80, t)
# get the tangent points
tx = py5.bezier_tangent(85, 10, 90, 15, t)
ty = py5.bezier_tangent(20, 10, 90, 80, t)
# calculate an angle from_ the tangent points
a = py5.atan2(ty, tx)
a += py5.PI
py5.stroke(255, 102, 0)
py5.line(x, y, py5.cos(a)*30+x, py5.sin(a)*30+y)
# the following line of code makes a line
# inverse of the above line
#line(x, y, cos(a)*-30+x, sin(a)*-30+y)
py5.stroke(0)
py5.ellipse(x, y, 5, 5)

def setup():
py5.no_fill()
py5.bezier(85, 20, 10, 10, 90, 90, 15, 80)
py5.stroke(255, 102, 0)
steps = 16
for i in range(0, steps+1):
t = i / steps
x = py5.bezier_point(85, 10, 90, 15, t)
y = py5.bezier_point(20, 10, 90, 80, t)
tx = py5.bezier_tangent(85, 10, 90, 15, t)
ty = py5.bezier_tangent(20, 10, 90, 80, t)
a = py5.atan2(ty, tx)
a -= py5.HALF_PI
py5.line(x, y, py5.cos(a)*8+x, py5.sin(a)*8+y)
Description#
Calculates the tangent of a point on a Bezier curve. There is a good definition of tangent on Wikipedia.
Underlying Processing method: bezierTangent
Signatures#
bezier_tangent(
a: float, # coordinate of first point on the curve
b: float, # coordinate of first control point
c: float, # coordinate of second control point
d: float, # coordinate of second point on the curve
t: float, # value between 0 and 1
/,
) -> float
Updated on March 06, 2023 02:49:26am UTC
