ortho()#
Sets an orthographic projection and defines a parallel clipping volume.
Examples#
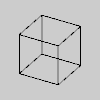
def setup():
py5.size(100, 100, py5.P3D)
py5.no_fill()
py5.ortho(-py5.width//2, py5.width//2,
-py5.height // 2, py5.height//2) # same as ortho()
py5.translate(py5.width//2, py5.height//2, 0)
py5.rotate_x(-py5.PI/6)
py5.rotate_y(py5.PI/3)
py5.box(45)
Description#
Sets an orthographic projection and defines a parallel clipping volume. All objects with the same dimension appear the same size, regardless of whether they are near or far from the camera. The parameters to this function specify the clipping volume where left and right are the minimum and maximum x values, top and bottom are the minimum and maximum y values, and near and far are the minimum and maximum z values. If no parameters are given, the default is used: ortho(-width/2, width/2, -height/2, height/2).
Underlying Processing method: ortho
Signatures#
ortho() -> None
ortho(
left: float, # left plane of the clipping volume
right: float, # right plane of the clipping volume
bottom: float, # bottom plane of the clipping volume
top: float, # top plane of the clipping volume
/,
) -> None
ortho(
left: float, # left plane of the clipping volume
right: float, # right plane of the clipping volume
bottom: float, # bottom plane of the clipping volume
top: float, # top plane of the clipping volume
near: float, # distance from the viewer to the nearest clipping plane
far: float, # distance from the viewer to the farthest clipping plane
/,
) -> None
Updated on February 29, 2024 00:18:21am UTC
