perspective()#
Sets a perspective projection applying foreshortening, making distant objects appear smaller than closer ones.
Examples#
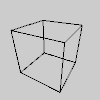
def setup():
py5.size(100, 100, py5.P3D)
# re-creates the default perspective
py5.no_fill()
fov = py5.PI/3.0
camera_z = (py5.height//2.0) / py5.tan(fov/2.0)
py5.perspective(fov, py5.width/py5.height,
camera_z/10.0, camera_z*10.0)
py5.translate(50, 50, 0)
py5.rotate_x(-py5.PI/6)
py5.rotate_y(py5.PI/3)
py5.box(45)
Description#
Sets a perspective projection applying foreshortening, making distant objects appear smaller than closer ones. The parameters define a viewing volume with the shape of truncated pyramid. Objects near to the front of the volume appear their actual size, while farther objects appear smaller. This projection simulates the perspective of the world more accurately than orthographic projection. The version of perspective without parameters sets the default perspective and the version with four parameters allows the programmer to set the area precisely. The default values are: perspective(PI/3.0, width/height, cameraZ/10.0, cameraZ*10.0) where cameraZ is ((height/2.0) / tan(PI*60.0/360.0)).
Underlying Processing method: perspective
Signatures#
perspective() -> None
perspective(
fovy: float, # field-of-view angle (in radians) for vertical direction
aspect: float, # ratio of width to height
z_near: float, # z-position of nearest clipping plane
z_far: float, # z-position of farthest clipping plane
/,
) -> None
Updated on March 06, 2023 02:49:26am UTC
